401 PreWork “Data Structures and Algorithms”
Notes
8 Commonly Used Data Structures
Arrays
An array is a structure of fixed-size, which can hold items of the same data type. It can be an array of integers, an array of floating-point numbers, an array of strings or even an array of arrays (such as 2-dimensional arrays). Arrays are indexed, meaning that random access is possible.
Array Operations:
- Traverse: Go through the elements and print them.
- Search: Search for an element in the array. You can search the element by its value or its index
- Update: Update the value of an existing element at a given index
Linked Lists
A linked list is a sequential structure that consists of a sequence of items in linear order which are linked to each other. Hence, you have to access data sequentially and random access is not possible. Linked lists provide a simple and flexible representation of dynamic sets.
- Singly linked list — Traversal of items can be done in the forward direction only.
- Doubly linked list — Traversal of items can be done in both forward and backward directions. Nodes consist of an additional pointer known as prev, pointing to the previous node.
- Circular linked lists — Linked lists where the prev pointer of the head points to the tail and the next pointer of the tail points to the head.
Operations for Linked Lists
- Search: Find the first element with the key k in the given linked list by a simple linear search and returns a pointer to this element
- Insert: Insert a key to the linked list. An insertion can be done in 3 different ways; insert at the beginning of the list, insert at the end of the list and insert in the middle of the list.
- Delete: Removes an element x from a given linked list. You cannot delete a node by a single step. A deletion can be done in 3 different ways; delete from the beginning of the list, delete from the end of the list and delete from the middle of the list.
Stacks
A stack is a LIFO (Last In First Out — the element placed at last can be accessed at first) structure which can be commonly found in many programming languages.
- Push: Insert an element on to the top of the stack.
- Pop: Delete the topmost element and return it.
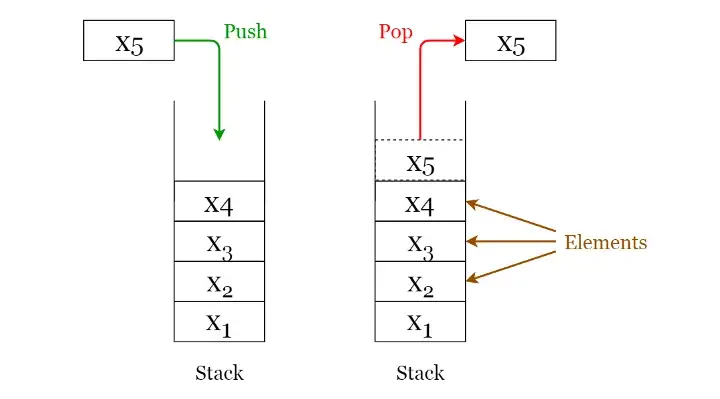
- Peek: Return the top element of the stack without deleting it.
- isEmpty: Check if the stack is empty.
- isFull: Check if the stack is full.
Queues
A queue is a FIFO (First In First Out — the element placed at first can be accessed at first) structure which can be commonly found in many programming languages. This structure is named as “queue” because it resembles a real-world queue
- Enqueue: Insert an element to the end of the queue.
- Dequeue: Delete the element from the beginning of the queue.
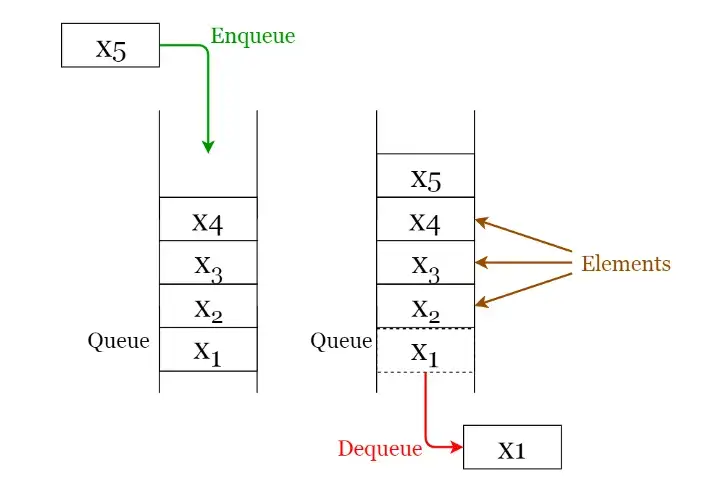
Hash Tables
A Hash Table is a data structure that stores values which have keys associated with each of them. Furthermore, it supports lookup efficiently if we know the key associated with the value. Hence it is very efficient in inserting and searching, irrespective of the size of the data. Direct Addressing uses the one-to-one mapping between the values and keys when storing in a table. However, there is a problem with this approach when there is a large number of key-value pairs. The table will be huge with so many records and may be impractical or even impossible to be stored, given the memory available on a typical computer. To avoid this issue we use hash tables.
A special function named as the hash function (h) is used to overcome the aforementioned problem in direct addressing. In direct accessing, a value with key k is stored in the slot k. Using the hash function, we calculate the index of the table (slot) to which each value goes. The value calculated using the hash function for a given key is called the hash value which indicates the index of the table to which the value is mapped. h(k) = k % m where:
- h: Hash function
- k: Key of which the hash value should be determined
- m: Size of the hash table (number of slots available). A prime value that is not close to an exact power of 2 is a good choice for m.
Trees
A tree is a hierarchical structure where data is organized hierarchically and are linked together.
Binary Search Tree (BST): A binary tree where data is organized in a hierarchical structure. This data structure stores values in sorted order.
- key: The value stored in the node.
- left: The pointer to the left child.
- right: The pointer to the right child.
- p: The pointer to the parent node.
Applications of Trees:
- Binary Trees: Used to implement expression parsers and expression solvers.
- Binary Search Tree: used in many search applications where data are constantly entering and leaving.
- Heaps: used by JVM (Java Virtual Machine) to store Java objects.
- Treaps: used in wireless networking.
Heaps
A Heap is a special case of a binary tree where the parent nodes are compared to their children with their values and are arranged accordingly.
2 Types of Heaps:
- Min Heap — the key of the parent is less than or equal to those of its children. This is called the min-heap property. The root will contain the minimum value of the heap.
- Max Heap — the key of the parent is greater than or equal to those of its children. This is called the max-heap property. The root will contain the maximum value of the heap.
Graphs
graphs consist of finite sets of vertices or nodes and a set of edges connecting these. The order of a graph is the number of vertices in the graph. The size of a graph is the number of edges in the graph.Two nodes are said to be adjacent if they are connected to each other by the same edge.
Directed Graph: A graph G is said to be a directed graph if all its edges have a direction indicating what is the start vertex and what is the end vertex.
Undirected Graphs: A graph G is said to be an undirected graph if all its edges have no direction. It can go in both ways between the two vertices. If a vertex is not connected to any other node in the graph, it is said to be isolated.
Big O
The name of the notation used to describe how efficient an algorithm is.
4 Important Rules about Big O:
- If you have different steps in the algorithm, you add up those steps
- Drop constants
- If different inputs, use different variables to represent them
- Drop non-dominant terms
Questions
-
What is 1 of the more important things you should consider when deciding which data structure is best suited to solve a particular problem? What am I using the data for? What format of data am I storing? How much data do I have?
-
How can we ensure that we’ll avoid an infinite recursive call stack? You need to provide a base case that lets the function exit a loop(tell the function to exit the loop)
Things I Want to Know More About
- Hash Tables
- Big O
- Binary Search Trees
Resources
- Video: Basic Recursion
- Video: Data Structures in 15 Minutes
- Video: Big ) Explained
- Basic Data Structures
- Why Big O