Course 201 Class Eight “CSS Layout”
CSS Flexbox
The Flexible Box Layout Model (flexbox) is a layout model designed for one-dimensional content. It excels at taking a bunch of items which have different sizes, and returning the best layout for those items.
This is the ideal layout model for this sidebar pattern. Flexbox not only helps lay the sidebar and content out inline, but where there’s not enough space remaining, the sidebar will break onto a new line. Instead of setting rigid dimensions for the browser to follow, with flexbox, you can instead provide flexible boundaries to hint how the content could display.
Flex layouts have the following features, which you will be able to explore in this guide.
- They can display as a row, or a column.
- They respect the writing mode of the document.
- They are single line by default, but can be asked to wrap onto multiple lines.
- Items in the layout can be visually reordered, away from their order in the DOM.
- Space can be distributed inside the items, so they become bigger and smaller according to the space available in their parent.
- Space can be distributed around the items and flex lines in a wrapped layout, using the Box Alignment properties.
- The items themselves can be aligned on the cross axis.
The key to understanding flexbox is to understand the concept of a main axis and a cross axis. The main axis is the one set by your flex-direction property. If that is row your main axis is along the row, if it is column your main axis is along the column. Flex items move as a group on the main axis. Remember: we’ve got a bunch of things and we are trying to get the best layout for them as a group. The cross axis runs in the other direction to the main axis, so if flex-direction is row the cross axis runs along the column.
You can do two things on the cross axis. You can move the items individually or as a group so they align against each other and the flex container. Also, if you have wrapped flex lines, you can treat those lines as a group in order to control how space is assigned to those lines. You will see how this all works in practice throughout this guide, for now just keep in mind that the main axis follows your flex-direction.
Questions
- Flexbox is designed for one-dimensional content. Explain what this means.
Being one dimensional means that flexbot only deals with columns and rows.
- Explain the difference between the main axis and cross axis.
The main axis is either row or column and defines the direction of how your flex items are placed in the container. Cross axis is perpendicular to the main axis.
- How can using certain properties of flexbox negatively impact accessibility?
You can use row-reverse or column-reverse and then the items on page do not match what an html screen reader will show. This can cause accesibility issues.
Why FlexBox
Specifying what elements to lay out as flexible boxes
To start with, we need to select which elements are to be laid out as flexible boxes. To do this, we set a special value of display on the parent element of the elements you want to affect. In this case we want to lay out the <article> elements, so we set this on the <section>:
section {
display: flex;
}
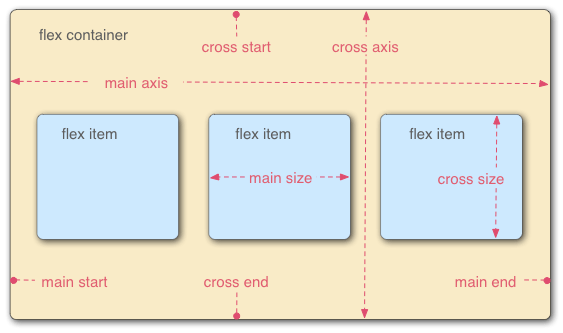
- The main axis is the axis running in the direction the flex items are laid out in (for example, as rows across the page, or columns down the page.) The start and end of this axis are called the main start and main end.
- The cross axis is the axis running perpendicular to the direction the flex items are laid out in. The start and end of this axis are called the cross start and cross end.
- The parent element that has display: flex set on it (the
<section>in our example) is called the flex container. - The items laid out as flexible boxes inside the flex container are called flex items (the
<article>elements in our example).
Question
-
What are some advantages of using flexbox over float?
Flexbos is responsive and mobile friendly, easier to use, and the margins do not collapse.
-
How does this topic connect with your long term goals?
Layout is very important to my long term goals because you need a basic understanding as a starting point to be able to add or change this on a website.
Resources
Return to the Table of Contents
